Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Parasitology
Plasmodium vivax
Ring
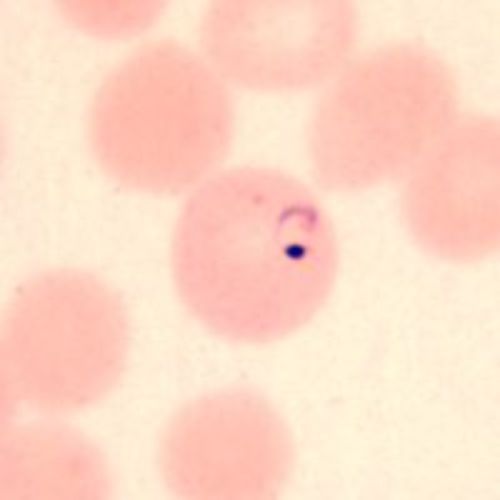
Ring
- Delicate ring
- RBC larger than normal
- Deformed
Growing trophozoite; Schüffner's dots
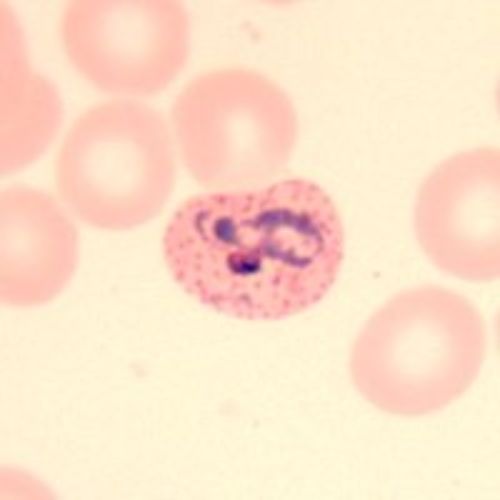
Growing trophozoite; Schüffner's dots
- Very amoeboid trophozoite
- Enlarged RBCs and deformed
- Schüffner's dots appear after 8-10 hours
Immature schizont
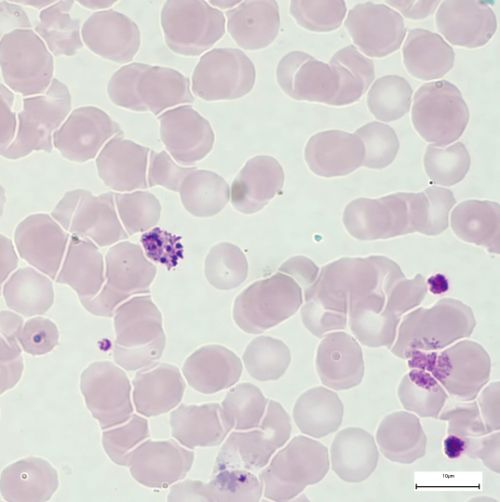
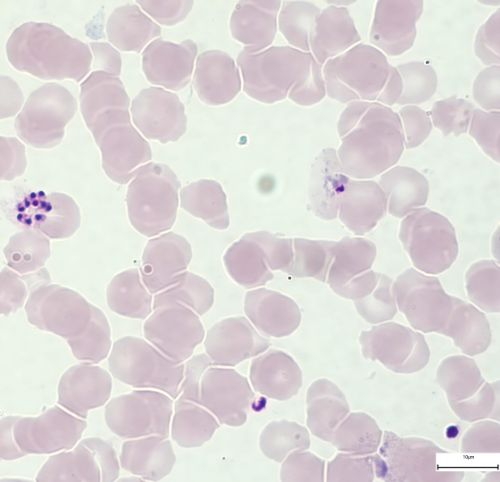
Immature schizont
- Looks like a growing trophozoite with several chromatins
- The single merozoite is not yet defined
Mature schizont
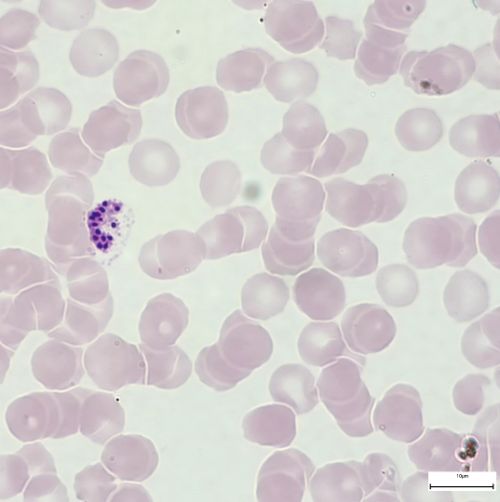
Mature schizont
- Contains 12-24 merozoites
- Pigment in 1 or 2 clumps
- Peripheral or central
Ruptured schizont
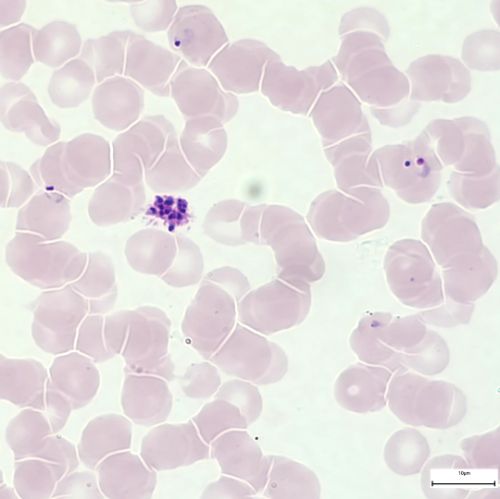
Ruptured schizont
- RBCs membran ruptured and the merozoites (up to 24) are set free to infect new RBCs
Macrogametocyte
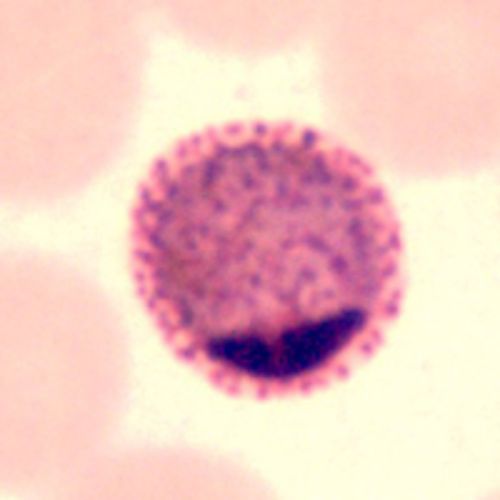
Macrogametocyte
- Chromatin small
- Eccentric and dark red
- Cytoplasm homogeneous
- Blue
- Without vacuoles
- Pigment scattered
- Macrogametocyte fills the RBC
Microgametocyte
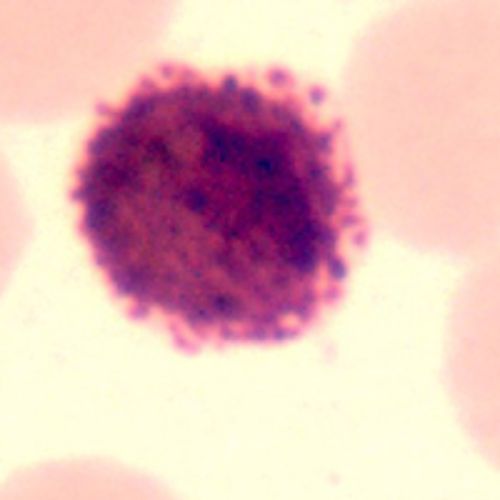
Microgametocyte
- Chromatin mass larger than in microgametocyte
- Eccentric or central
- Diffuse
- Light red
Cytoplasm from light blue to pink
- Pigment finer
- Scattered
- Microgametocyte is smaller than the RBC
Exflagellation
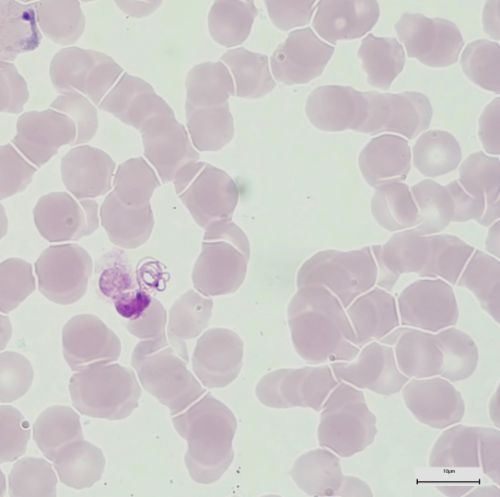
Exflagellation
- Under certain circumstances the microgametocyte of P. vivax can exflagellate in a thin film of human blood
- A process that normally takes place in the vector's gut
- There the microgamete (male) undergo a nuclear division and become motile to find and to penetrate the female macrogamete